Order 500+ lab tests online — no doctor or insurance needed
Arthritis and Inflammation Tests
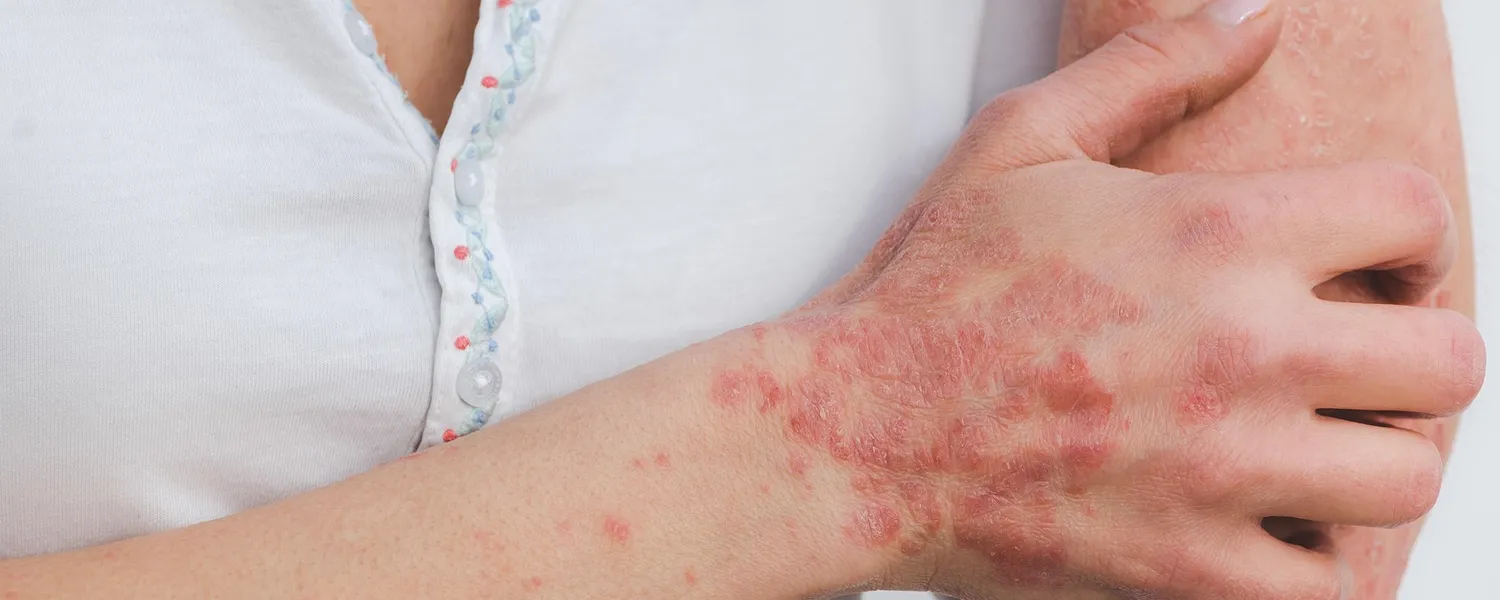
Psoriasis is far more than a skin-deep condition. At its core, it’s an immune-mediated disease characterized by chronic inflammation, leading to the hallmark symptoms of red, scaly skin plaques. But for those living with psoriasis, understanding and managing the underlying inflammation is key—not just for clearer skin, but for overall health and well-being.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore:
Psoriasis is primarily driven by an overactive immune response. In people with psoriasis, certain immune cells (T-cells) mistakenly target healthy skin cells as if they’re fighting off an infection. This triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals (cytokines), which accelerate the growth cycle of skin cells and produce the classic plaques and scales.
Several factors can spark or worsen inflammation in psoriasis, including:
It’s important to realize that the inflammation in psoriasis isn’t limited to the skin. Chronic inflammation can affect the joints (psoriatic arthritis) and is associated with increased risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Managing psoriasis typically involves treatments aimed at reducing inflammation and slowing skin cell turnover. Treatment options include:
Consistently using prescribed medications and following up with your healthcare provider is crucial for long-term control of inflammation.
While medical treatment is essential, lifestyle choices can make a significant difference:
It’s vital to stay in close communication with your healthcare provider. Contact your doctor if you:
Psoriasis is a lifelong condition, but managing chronic inflammation is possible with a combination of medical treatments, healthy lifestyle choices, and regular medical support. By understanding the mechanisms of inflammation and actively working to reduce it, you can improve your symptoms, lower your risk of related health problems, and enjoy a better quality of life.
Remember: Every individual’s experience with psoriasis is unique. Work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized, comprehensive plan for managing inflammation and living well with psoriasis.
Comprehensive Remedies for Lower Back Pain: A Holistic Approach Managing Chronic Inflammation with Psoriasis: An In-Depth Guide Understanding Myasthenia Gravis Autoimmune Neuromuscular Disease
Acetylcholine Receptor Binding Antibody (AChR) Test ANA Blood Test (Antinuclear Antibodies) Autoimmune Disorder Panel C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test C-Reactive Protein (CRP), High Sensitivity ESR Test (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) Lupus Panel Rheumatoid Arthritis Test - Rheumatoid Factor (RF)